Trusted by 200+ industry leaders across the globe





Trusted by 200+ industry leaders across the globe





Spotlight Data gives you clear answers about which activities help your business grow and which don't. Follow what has worked for you in the past and stop wasting time in endless meetings.
Book a demo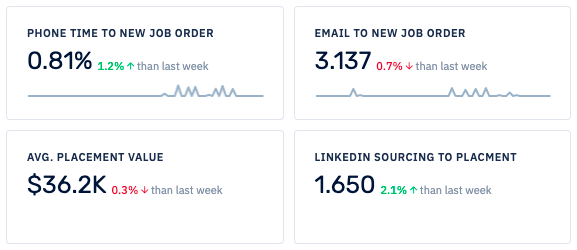

Spotlight Data gives you clear answers about which activities help your business grow and which don't. Follow what has worked for you the past and stop wasting time in endless meetings.
Book a demoYou can track your recruiter and team goals accurately in real-time. See who is on track and who needs help to meet their targets.
Book a demoYou can track your recruiter and team goals accurately in real-time.See who is on track and who needs help to meet their targets.
Book a demoOne size never fits all. See which recruiters need help with their phone calls, emails, or candidate pipeline and create custom training programs.
Book a demo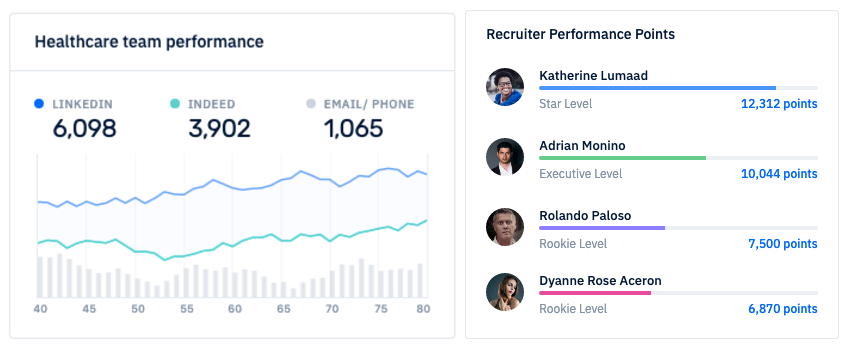

One size never fits all. See which recruiters need help with their phone calls, emails, or candidate pipeline and create custom training programs.
Book a demo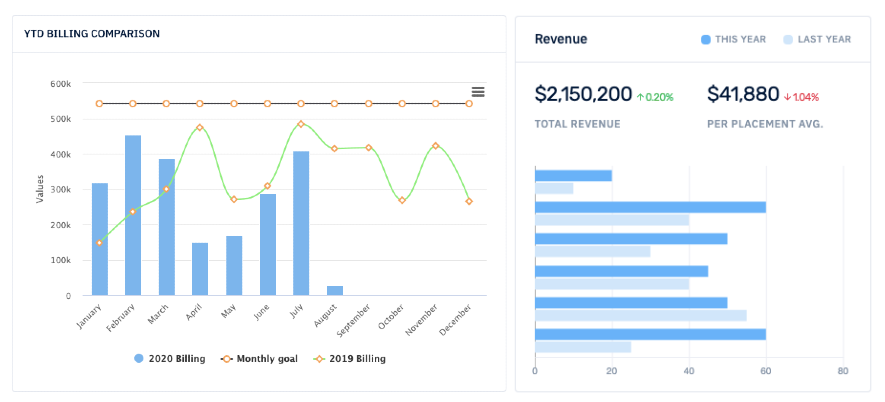
Improve the quality and quantity metrics of your sales and placement process and get happier clients, increased revenue, and a better brand image in return.
Book a demo
Improve the quality and quantity metrics of your sales and placement process and get happier clients, increased revenue, and better brand image in return.
Book a demoSpotlight Data technology and tools are specially designed to help recruiting and staffing firms transform into data-driven businesses. Give your search firm and team the help they need to perform better in these competitive times.
Book a free demo now
When it pertains to effective onboarding, utilizing the right employee training materials is vital for success. You’ll find that thorough

Stuart Gentle Publisher at Onrec 15 Oct 2025|StatisticsChristmas job searches hit nine-year high as employers prepare for busy festive seasonMore jobseekers

To improve your business performance, it’s vital to implement specific strategies that can drive growth and efficiency. Start by analyzing